We use cookies to improve and analyse your browsing experience on our web. You can accept these cookies, reject them or choose your settings by clicking on the corresponding buttons. Please note that rejecting cookies may affect your browsing experience. For more information you can consult our Cookies policy.
Cookies are an essential part of how our web works. The main goal of cookies is to make your browsing experience more comfortable and efficient and to improve our services and the web itself.
Here you can find all the information about the cookies we use and you can activate and/or deactivate them according to your preferences, except for those cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of the web. Blocking some cookies may affect your experience on the web and how the site works. For more information you can visit our Cookie Policy.
These Cookies are necessary for the web to function and cannot be disabled on our systems. They are generally only set up in response to actions you may take such as requesting services, setting your privacy preferences, logging in or completing forms. You can set your browser to block or warn you about these cookies, but some parts of the web will not work. Information about Cookies.
These Cookies allow us to count the number of visits and traffic sources so that we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to find out which pages are the most popular and least popular, and to see how visitors move around the web. All information collected by these Cookies is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these Cookies we will not know when you visited our web. Information about Cookies.
These cookies are used to analyse your activity in order to show you personalised advertisements. Information about Cookies.
Change theme

Revision mode

In this unit, we have seen different types of structural elements. Now, let's look at the most important ones according to their function.
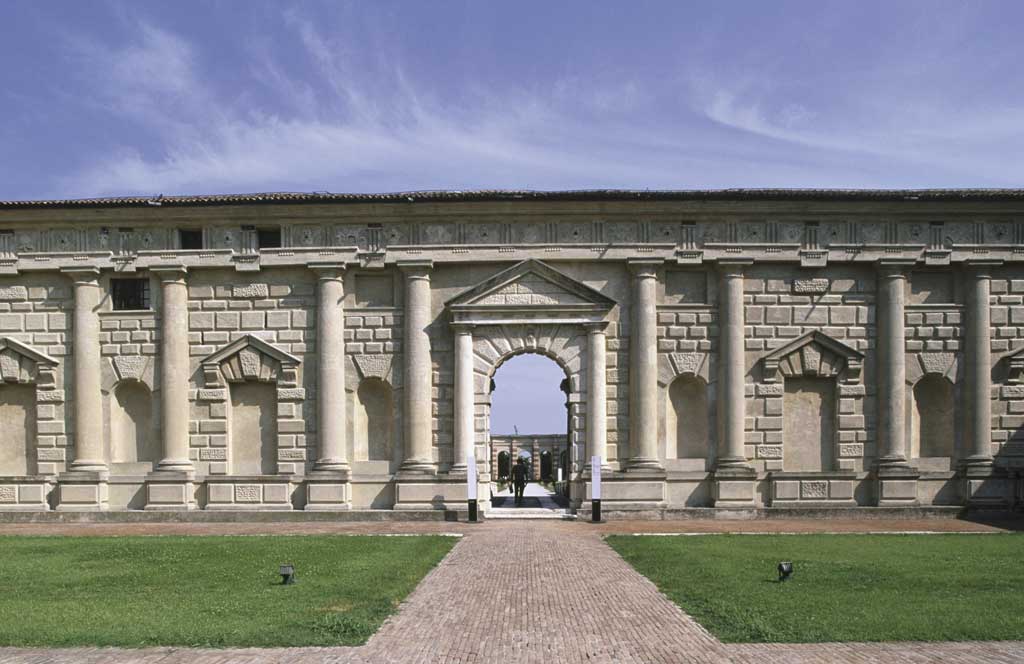


These are vertical elements that support the weight of the structure on top of them and transfer it to a lower level or to the foundations.
They resist compression stress and, depending on the historical period, are made of stone, reinforced concrete or metal.
These are linear horizontal elements that keep a space between two supports.
These elements bear bending stress and nowadays they are made of steel or reinforced concrete. Remember that concrete resists compression and the steel rebar framework resists traction.
In ancient times, when stone was the most common construction material, lintels could not be very long, so the openings they made were very small.

Conjunction so to express reason for something
...resist compression stress and so are usually made of materials like stone
These are two –or three– dimensional curved elements, which are used to cover the space between two walls or columns. The pieces in them resist compression stress and so are usually made of materials like stone.
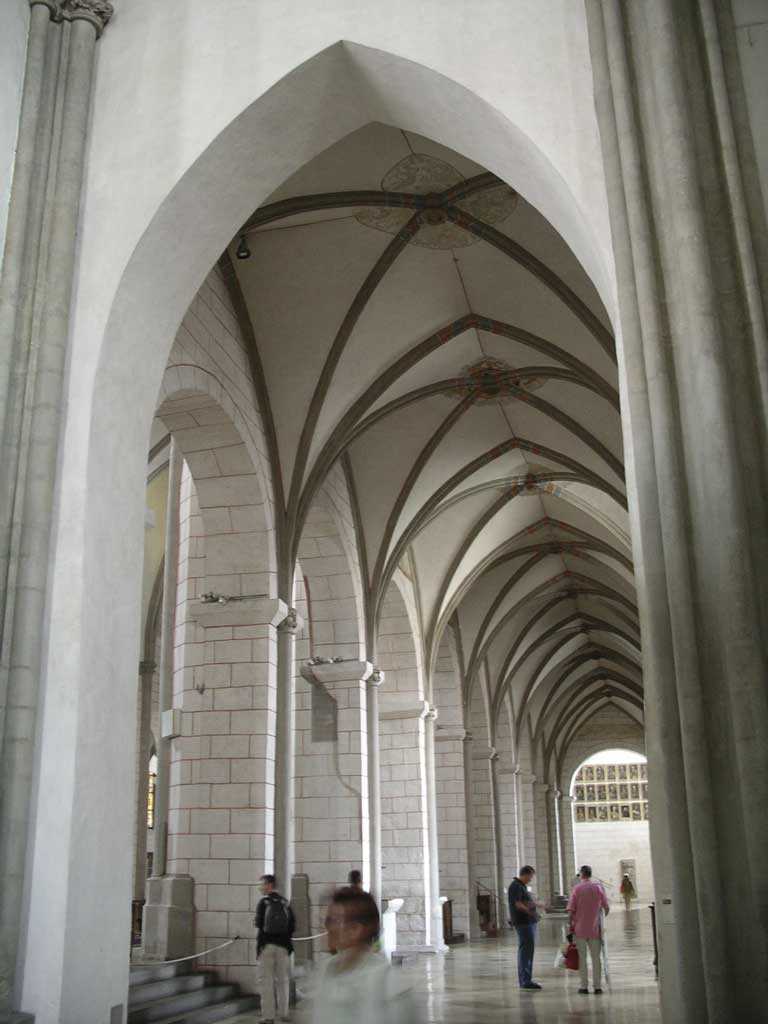



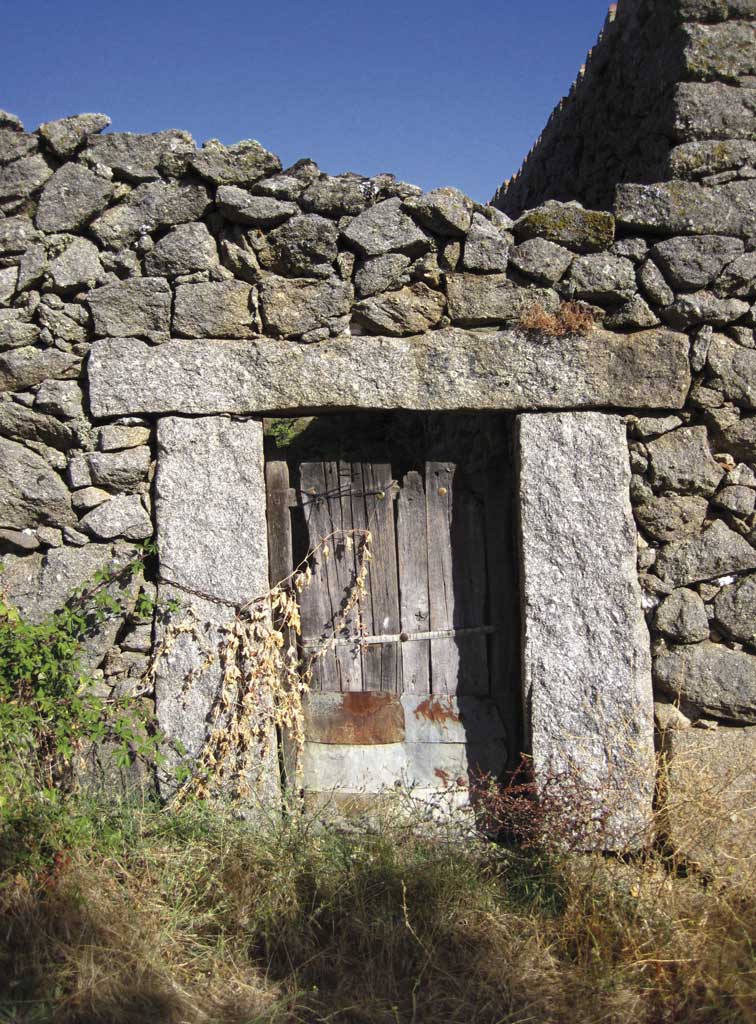
These are used to hold up the loads of arches and vaults.
Nowadays we use reinforced concrete as well as stone.


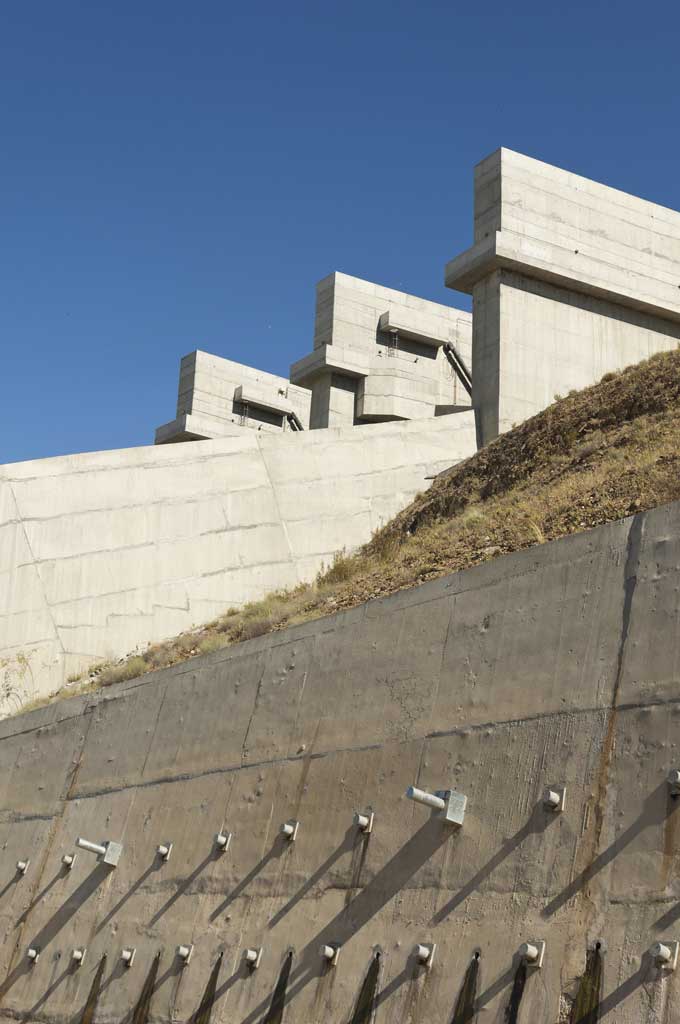
These are vertical elements that transfer loads to the ground.


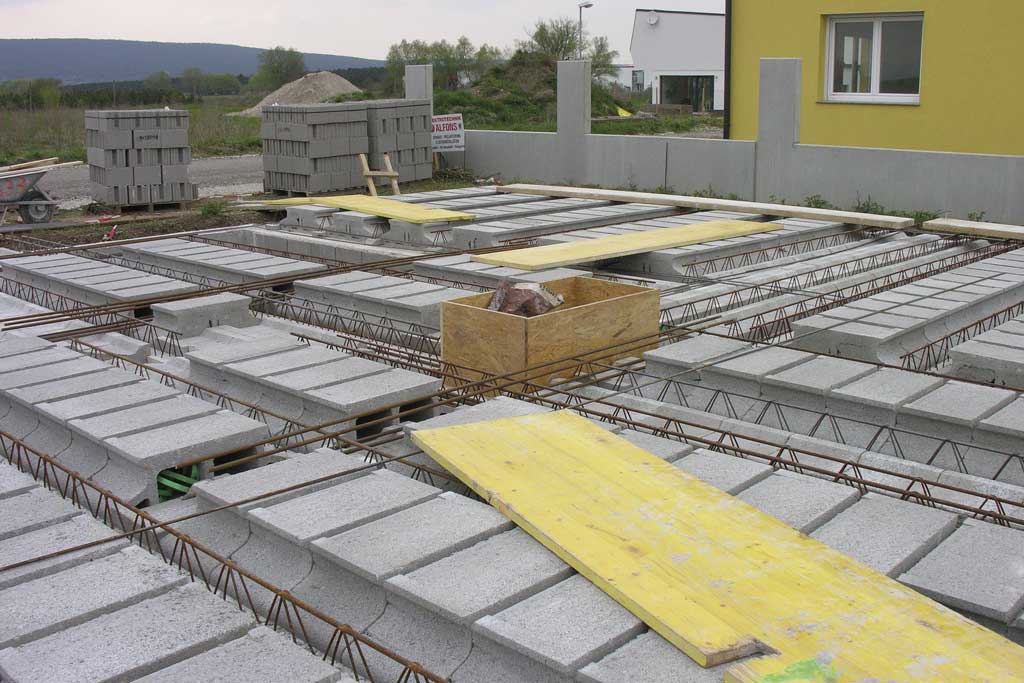
These are horizontal elements working in two directions. They transfer the loads that the rest of the structure bears and they resist bending stress. They are made up of:

The purpose of these elements is to distribute the load of the structure, building or bridge so that it does not sink. These elements together are called the foundations. There are different types:
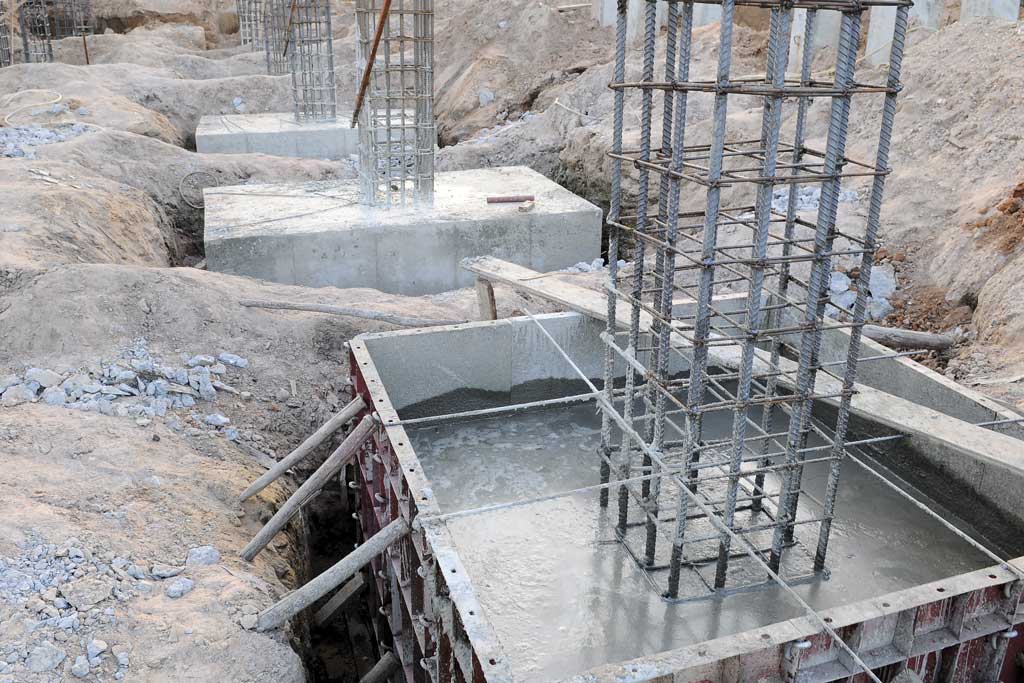
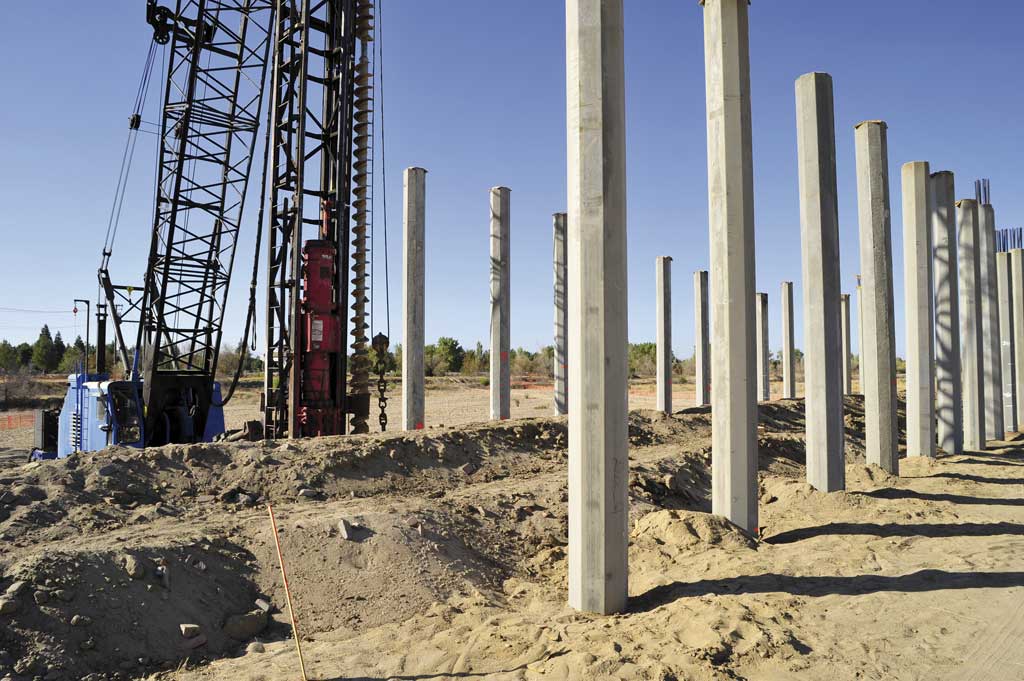


Structural elements are classified by the following functions:
These are linear elements, normally steel cables, whose function is to resist traction stress. They are used in suspended constructions and in bracing.
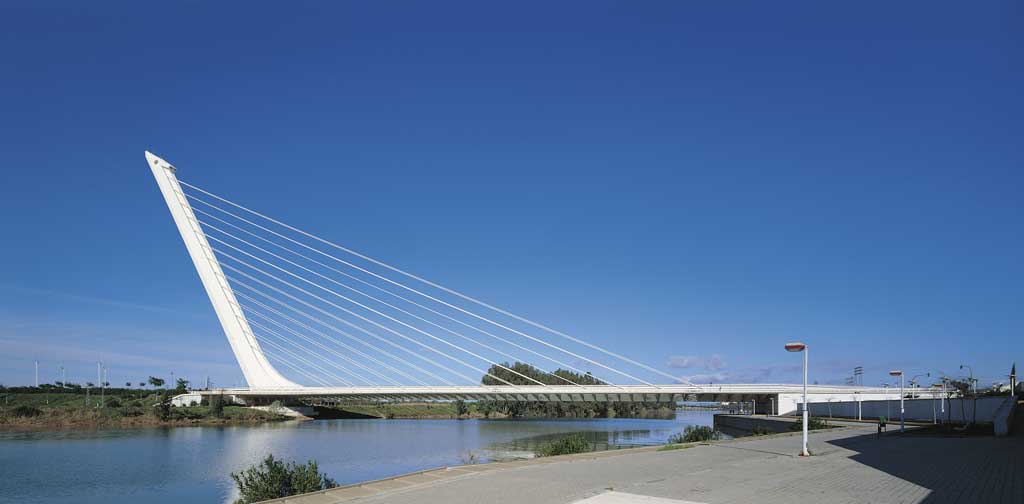
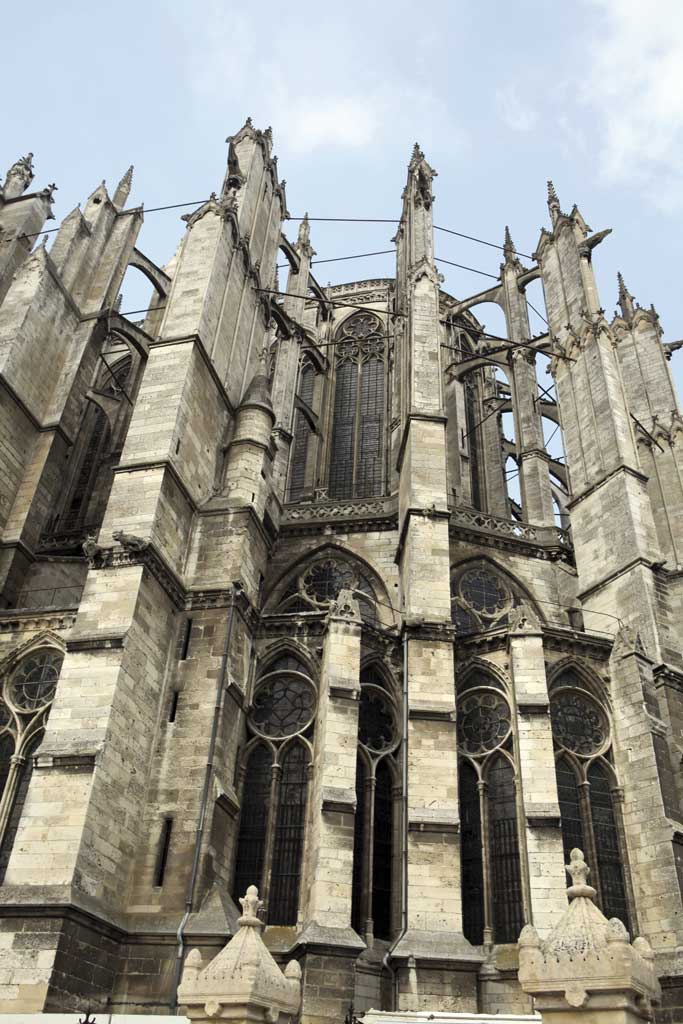


Activity 33
Where is the centring of the arch in construction in the picture?
Activity 34
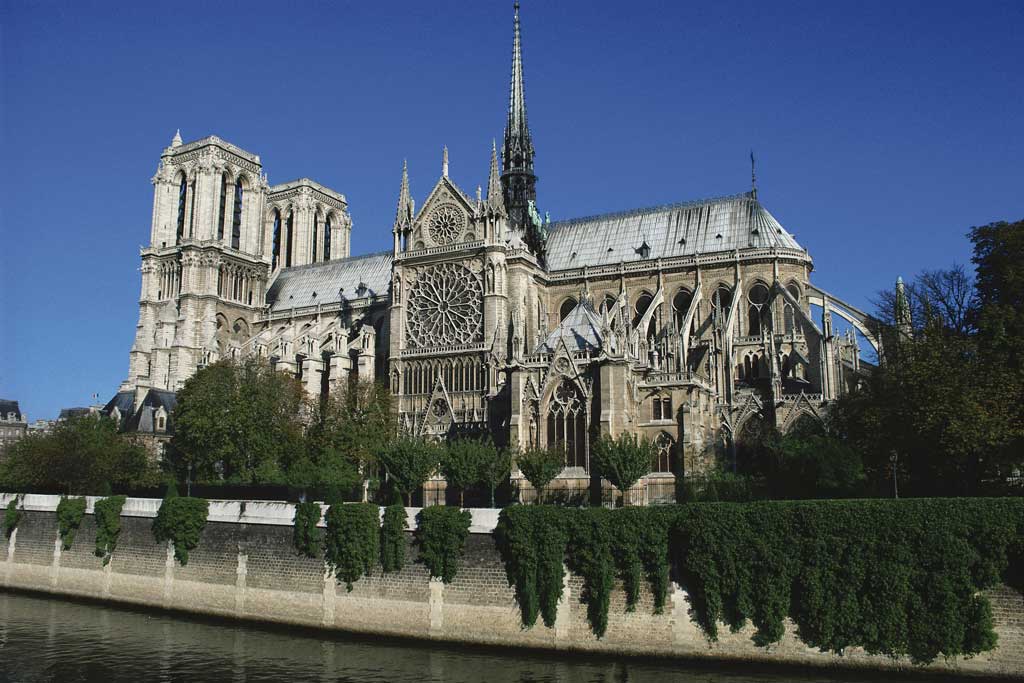
What types of arches can you see on the front of this building?
Activity 35
Select the correct statement regarding the types of stress a structure bears.
Activity 36
Using the development plan of an arch stone you can see, build an arch using five pieces. Put it together horizontally on a piece of cardboard. Raise it carefully and check that it stays up by itself without any glue.
Activity 37
In the photo, we can see the formwork of the main beams of a concrete slab. Find the start rebars of the pillar, the rebars of the beams, the temporary jack posts and the safety net. Match to make sentences.
Activity 38
Identify the structural elements. Match the material used in each part of the structure with the types of stress each part bears.