We use cookies to improve and analyse your browsing experience on our web. You can accept these cookies, reject them or choose your settings by clicking on the corresponding buttons. Please note that rejecting cookies may affect your browsing experience. For more information you can consult our Cookies policy.
Cookies are an essential part of how our web works. The main goal of cookies is to make your browsing experience more comfortable and efficient and to improve our services and the web itself.
Here you can find all the information about the cookies we use and you can activate and/or deactivate them according to your preferences, except for those cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of the web. Blocking some cookies may affect your experience on the web and how the site works. For more information you can visit our Cookie Policy.
These Cookies are necessary for the web to function and cannot be disabled on our systems. They are generally only set up in response to actions you may take such as requesting services, setting your privacy preferences, logging in or completing forms. You can set your browser to block or warn you about these cookies, but some parts of the web will not work. Information about Cookies.
These Cookies allow us to count the number of visits and traffic sources so that we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to find out which pages are the most popular and least popular, and to see how visitors move around the web. All information collected by these Cookies is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these Cookies we will not know when you visited our web. Information about Cookies.
These cookies are used to analyse your activity in order to show you personalised advertisements. Information about Cookies.
Change theme

Revision mode

The Moon is a satellite that was possibly formed when a giant object planet, named Theia, hit the Earth 4.5 billion (4500 million) years ago. A piece of the Earth broke off and remained in orbit around the Earth, held by the force of gravity.
The Moon has an average radius of 1738 km. The average distance between the Moon and the Earth is 384400 km, although every year it moves away from our planet by almost 4 cm.
Like other celestial bodies, the Moon moves in two ways: revolution and rotation. Its revolution around the Earth takes 27.32 Earth days. This is the same time it takes the Moon to rotate once on its axis. So, a lunar day is the same length as a lunar year. For this reason, the side of the Moon we see from Earth is always the same.

The Moon does not produce its own light, but it reflects the light from the Sun. Depending on the position of the Moon in its orbit around the Earth, we see a different part of the side that is illuminated.
23.24.24.png?idcurso=626939)
The repetition of the phases of the Moon is called a lunar month.
One lunar month lasts about 29 days. So there are 12 lunar months.
To adjust the days to the calendar, as we do with leap years, every two or three years there is a lunar year with 13 full moons.
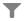
In the system made up of the Sun, the Earth and the Moon, an eclipse occurs when all three are aligned. Depending on the amount of the Sun or Moon that is hidden from sight, an eclipse can be total or partial.

On average, there are a minimum of four eclipses a year: two solar eclipses and two lunar eclipses.
 |
 |
|
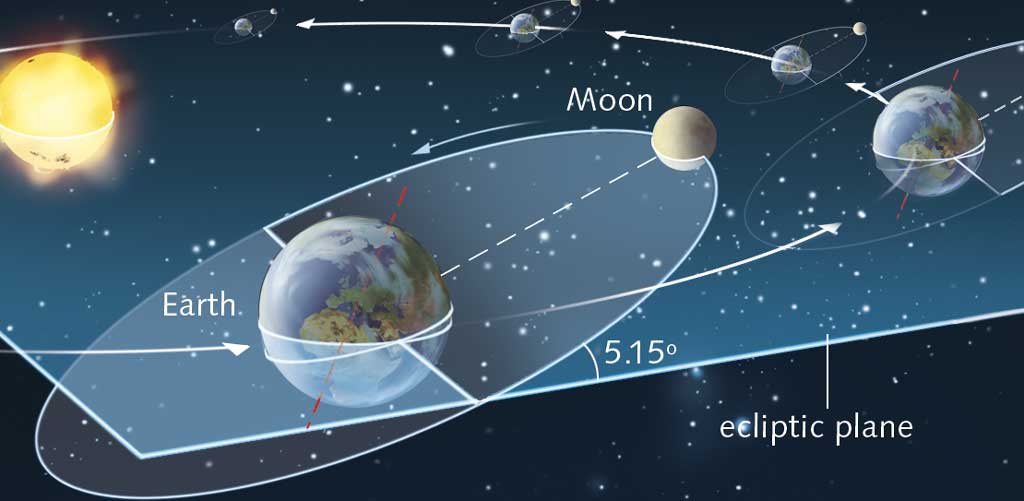
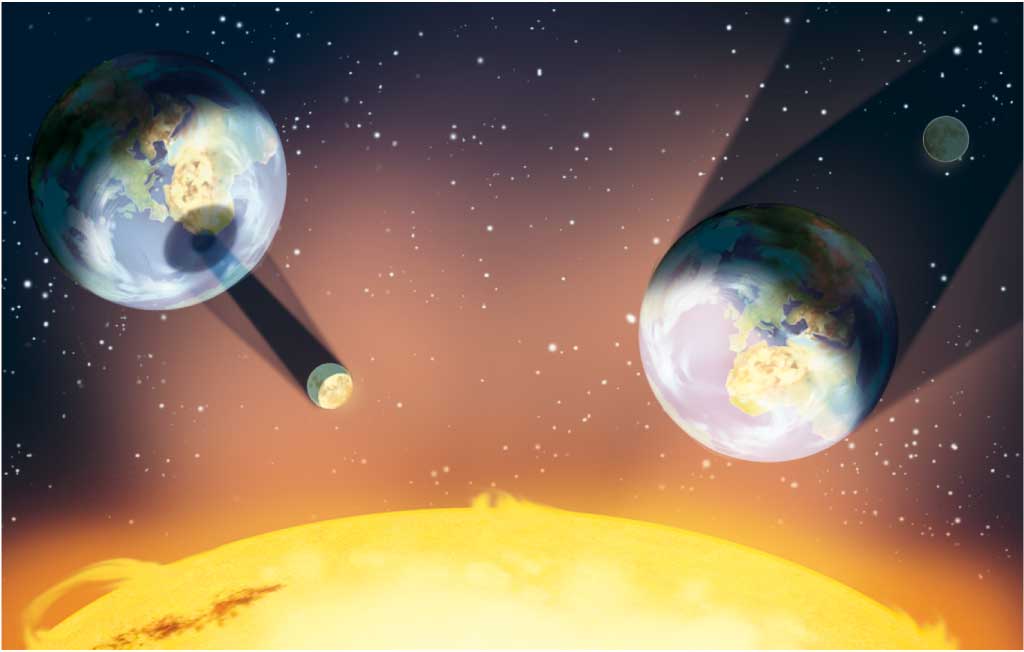
When the sea level rises, high tides are created (1). They occur on the side of the Earth facing the moon and on the opposite side. When the sea level falls, low tides (2) are created. They occur on the other two opposing sides. |
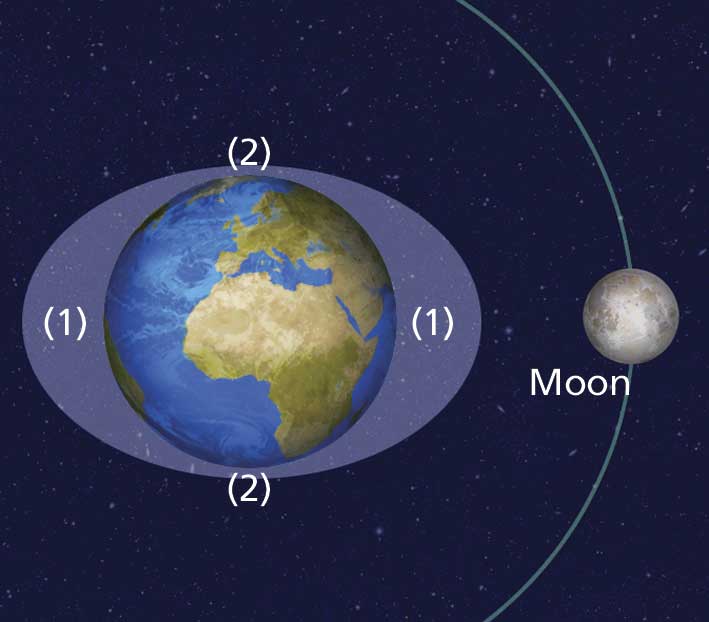
When the Moon, Earth and Sun are aligned, high and low tides are stronger (very high and very low). These are spring tides (3). In contrast, when the Moon and the Sun form a 90º angle with respect to the Earth, the Sun counteract the Moon’s gravitational pull. The tides are weaker. These are neap tides (4). |
Activity 29
Match the sentences halves for a better understanding of the "phases of the Earth".
Activity 30
Look at the diagram. Listen and name the phases of the Moon.
Activity 31
Why can’t there be a solar or lunar eclipse in the first quarter and the last quarter of the moon’s phases?
Activity 32
Classify the characteristics of spring and neap tides in order to find out the difference between them.