We use cookies to improve and analyse your browsing experience on our web. You can accept these cookies, reject them or choose your settings by clicking on the corresponding buttons. Please note that rejecting cookies may affect your browsing experience. For more information you can consult our Cookies policy.
Cookies are an essential part of how our web works. The main goal of cookies is to make your browsing experience more comfortable and efficient and to improve our services and the web itself.
Here you can find all the information about the cookies we use and you can activate and/or deactivate them according to your preferences, except for those cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of the web. Blocking some cookies may affect your experience on the web and how the site works. For more information you can visit our Cookie Policy.
These Cookies are necessary for the web to function and cannot be disabled on our systems. They are generally only set up in response to actions you may take such as requesting services, setting your privacy preferences, logging in or completing forms. You can set your browser to block or warn you about these cookies, but some parts of the web will not work. Information about Cookies.
These Cookies allow us to count the number of visits and traffic sources so that we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to find out which pages are the most popular and least popular, and to see how visitors move around the web. All information collected by these Cookies is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these Cookies we will not know when you visited our web. Information about Cookies.
These cookies are used to analyse your activity in order to show you personalised advertisements. Information about Cookies.
Change theme

Revision mode

Gorillas, chimpanzees and human beings all belong to a group of mammals called primates. These species, including modern humans, descend from a common ancestor.
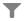
Hominisation began with the appearance of a bipedal primate species in east Africa. The members of this species walked on their back legs and are therefore considered the first hominids.
The most significant anatomical changes that occurred during hominisation were:
Genes are the part of a cell where an individual's physical characteristics are stored. This is the genetic information that children inherit from their parents. If a change occurs in this genetic information (a mutation), this can be passed on to the next generation. If this change becomes hereditary, this species changes or a new species is created.
When two species (the one that has mutated and the original one) share the same environment, the one that is least adapted will probably decrease in number until it disappears. This explains why we are the only surviving hominids. This theory is called evolution by natural selection and was developed by the British naturalist Charles Darwin.
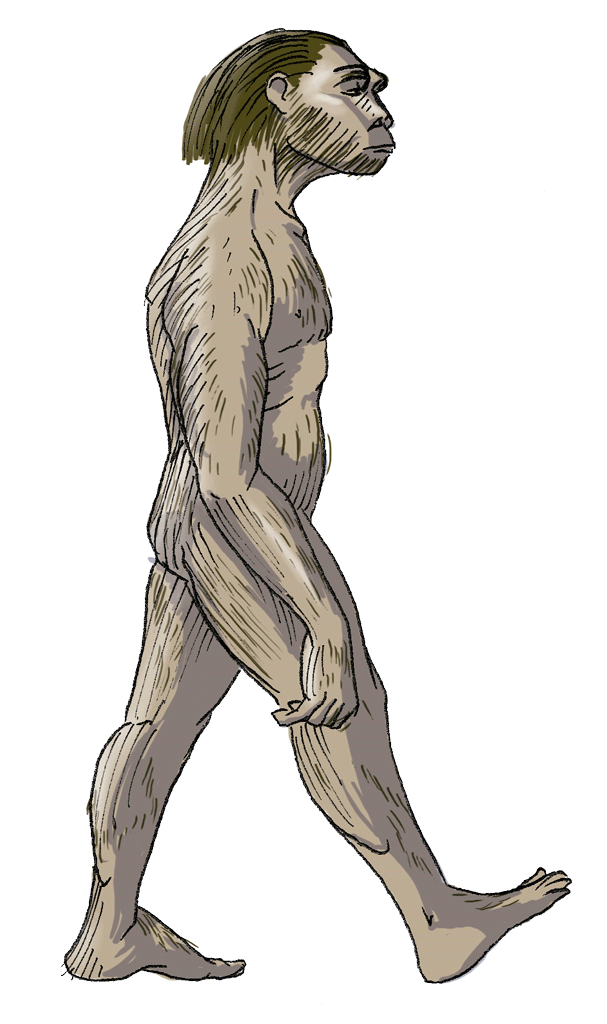
During the time of Australopithecus, the climate changed and the wooded areas where they lived became savannahs with less vegetation. It became increasingly difficult to obtain food. The genus Homo adapted best to this new situation.
Activity 1
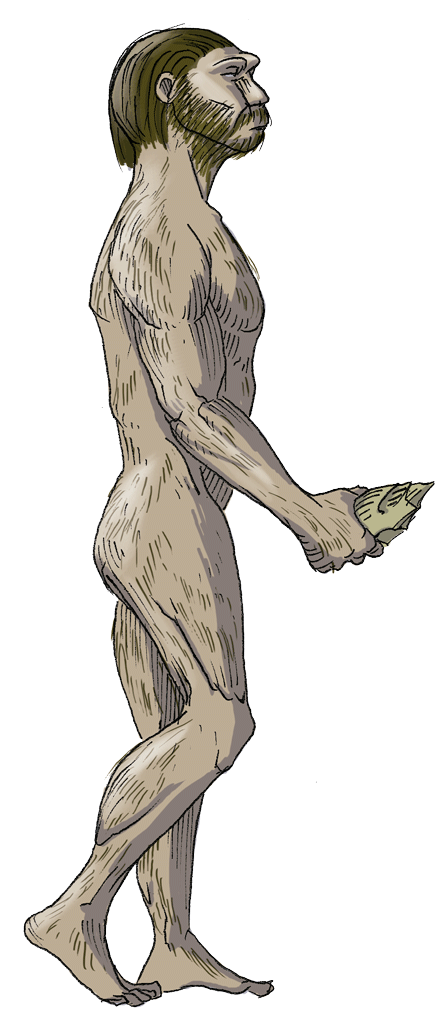
Look at the information about the evolution of hominids.
Activity 2
Which change in the process of hominisation do you think was the most important? Explain why.
Activity 3
Why do you think that walking upright was so important in the process of hominisation?
Activity 4
The development of language is attributed to changes in the larynx. What other change(s) could it be attributed to?
Activity 5
Think about how natural selection works. Why do you think that other species of hominids have not survived but some species of less-evolved primates, such as gorillas, have?