We use cookies to improve and analyse your browsing experience on our web. You can accept these cookies, reject them or choose your settings by clicking on the corresponding buttons. Please note that rejecting cookies may affect your browsing experience. For more information you can consult our Cookies policy.
Cookies are an essential part of how our web works. The main goal of cookies is to make your browsing experience more comfortable and efficient and to improve our services and the web itself.
Here you can find all the information about the cookies we use and you can activate and/or deactivate them according to your preferences, except for those cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of the web. Blocking some cookies may affect your experience on the web and how the site works. For more information you can visit our Cookie Policy.
These Cookies are necessary for the web to function and cannot be disabled on our systems. They are generally only set up in response to actions you may take such as requesting services, setting your privacy preferences, logging in or completing forms. You can set your browser to block or warn you about these cookies, but some parts of the web will not work. Information about Cookies.
These Cookies allow us to count the number of visits and traffic sources so that we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to find out which pages are the most popular and least popular, and to see how visitors move around the web. All information collected by these Cookies is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these Cookies we will not know when you visited our web. Information about Cookies.
These cookies are used to analyse your activity in order to show you personalised advertisements. Information about Cookies.
Change theme

Revision mode

Hess's observations about the extension of the ocean floor, along with the analysis of the global distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes, led to the theory of plate tectonics:

With the new information about the ocean floor, earthquake and volcano distribution, it was clear to Hess that the whole lithosphere (the continental and oceanic) was constantly moving, and not just the continents, as Wegner had thought. Recently, thanks to global positioning system (GPS), the movements of the plates have been verified.
Plate tectonics explained many geological phenomena that appeared not to be related to each other:
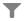
In addition to describing the movement of the continents to their present position, plate tectonics allows us to make predictions about their future movement, as shown in the diagram below:
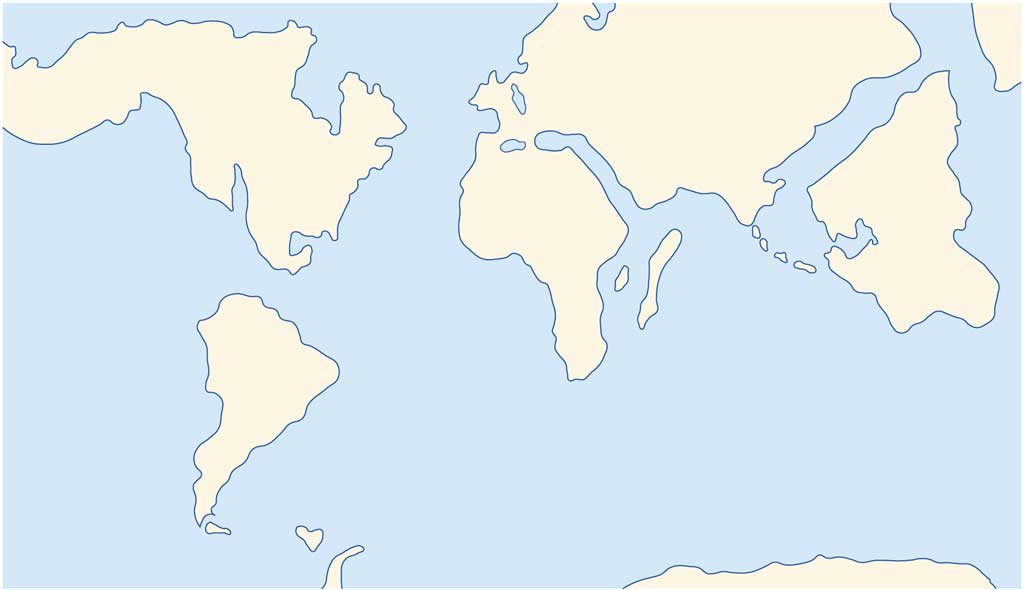
The theory of plate tectonics has been accepted by the scientific community for more than 50 years, even though it is still not completely clear how the movements of the plates are produced. The current theory of plate movement has evolved over time from the original hypothesis.
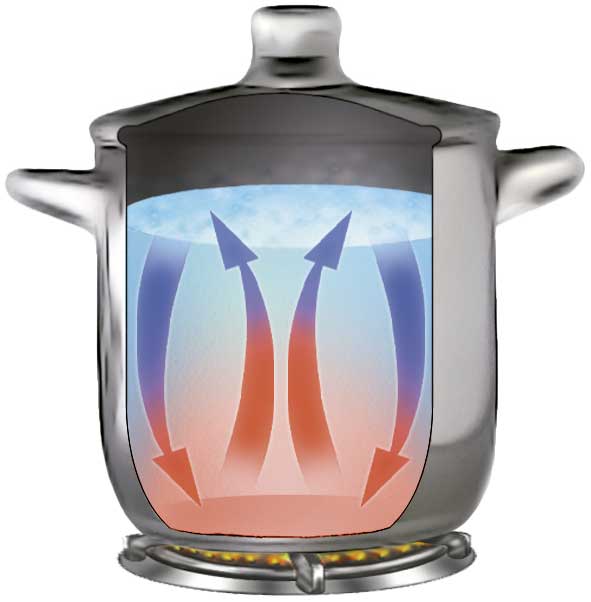

It was widely accepted that the lithosphere 'floats' on the asthenosphere. It was thought that the convection currents in the asthenosphere caused tectonic plate movement. It was believed that in the areas where hot currents rise and separate, ridges are formed.In the areas where currents cool and descend, trenches are formed.
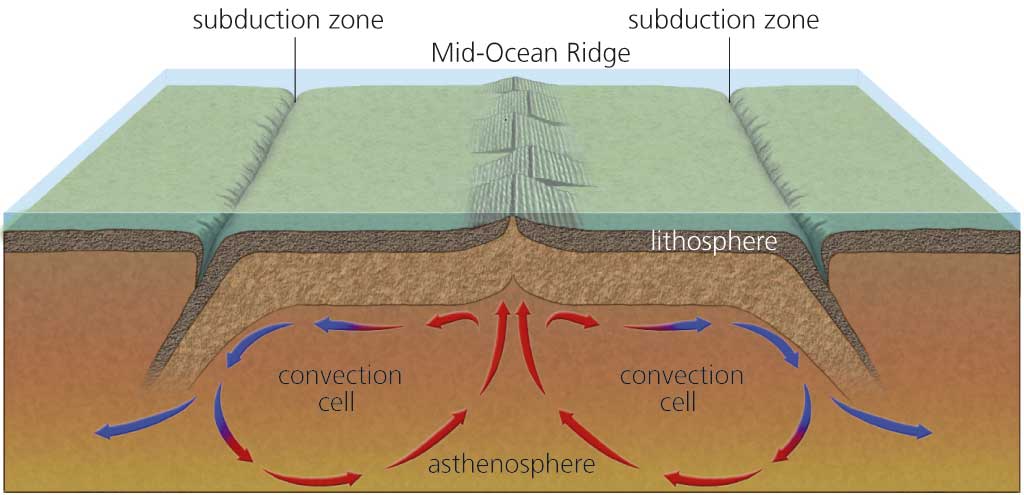
New seismic tomography techniques have increased scientists' understanding of the dynamics of the Earth's mantle and how the plates move. The lithospheric plates do not just float on the asthenosphere, but also actively contribute to their own movement in two ways:
In conclusion, heat rises from the core and makes the mantle ductile. It also generates convection currents in the mantle. These convection currents, combined with the forces of gravity and weight that act on the plate, cause the plates to move.
Wegener had no idea that there was at least one other supercontinent before the formation of Pangaea.
Canadian geologist John Tuzo Wilson (1909-1993) was the first to propose its existence. He suggested that throughout the history of the Earth there have been two cyclic processes of rifting and reuniting of supercontinents, this process is called the Wilson cycle.
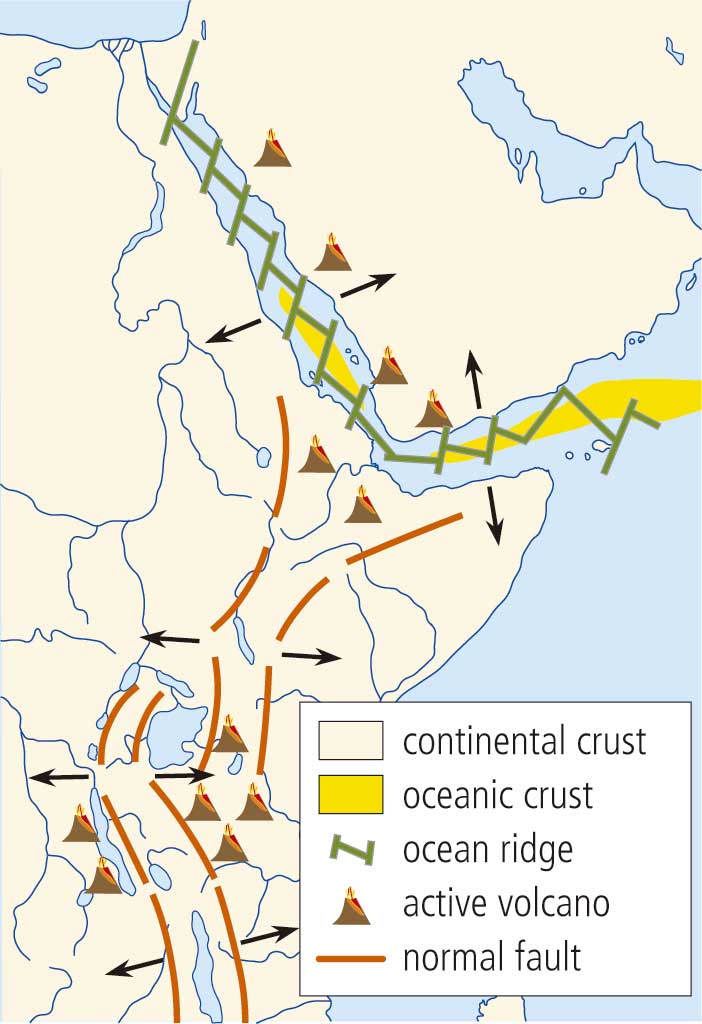
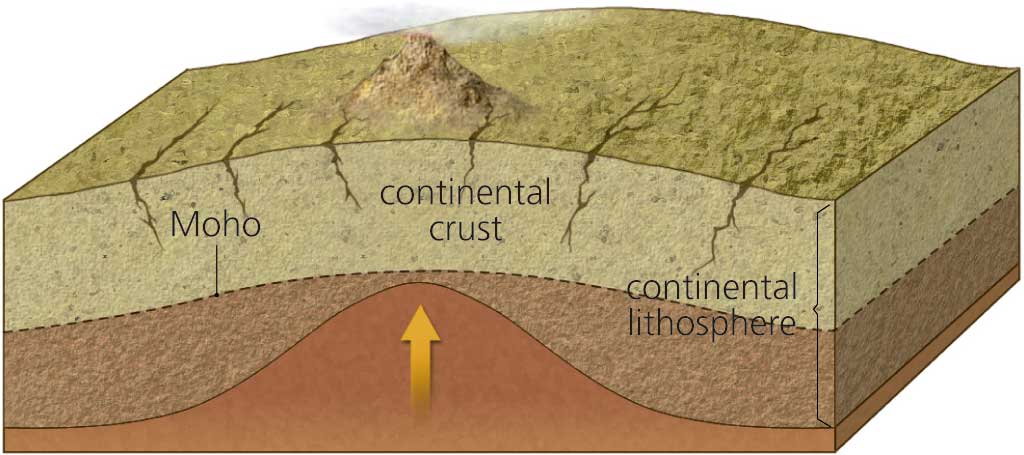
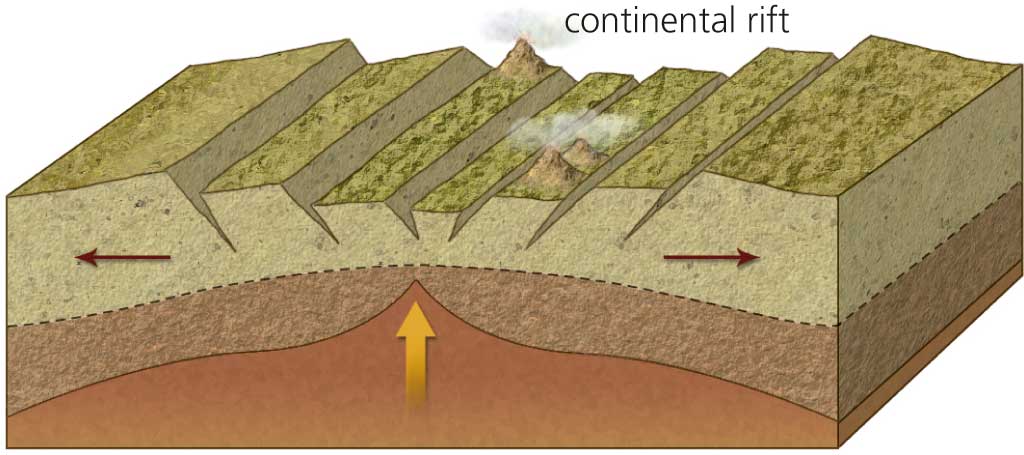
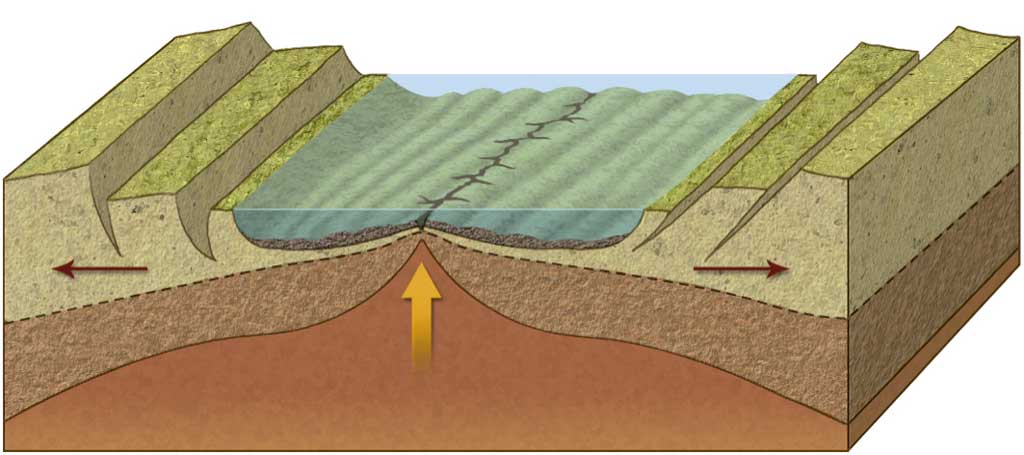
A clear example of continental rifting is found in the Rift Valley in East Africa. As you can see on the map on the left, the continental rift is at a divergent plate boundary. When the plates move apart, magma rises up through the fractures as lava, pushing the continental lithosphere on either side further apart. If the process of rifting continues, this continent will end up splitting in two.
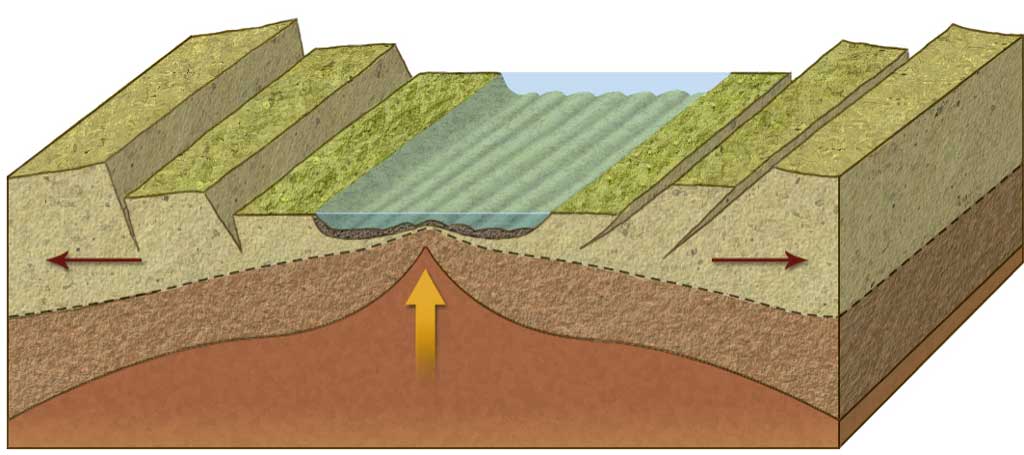
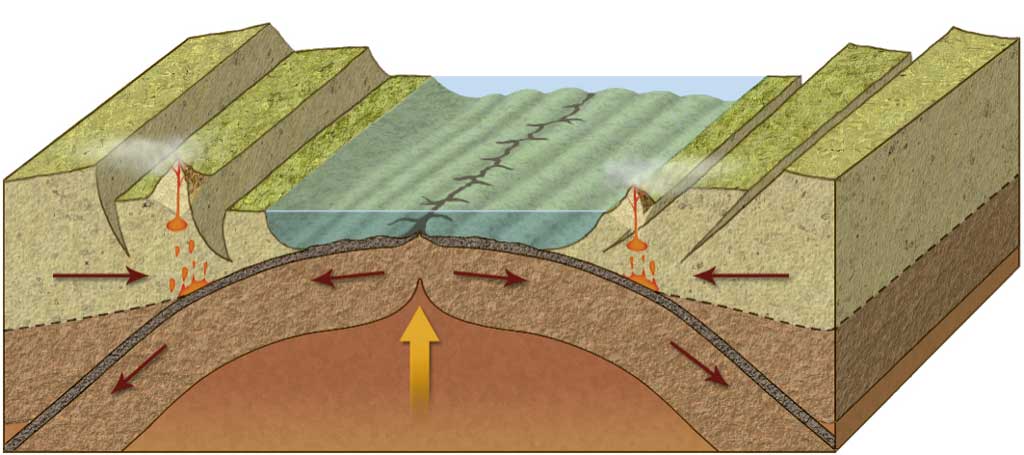
This is what has happened in the Red Sea. The Red Sea Rift separates the Arabian Peninsula from Africa. It once was a continental rift, but now it is an oceanic rift, generating oceanic lithosphere.
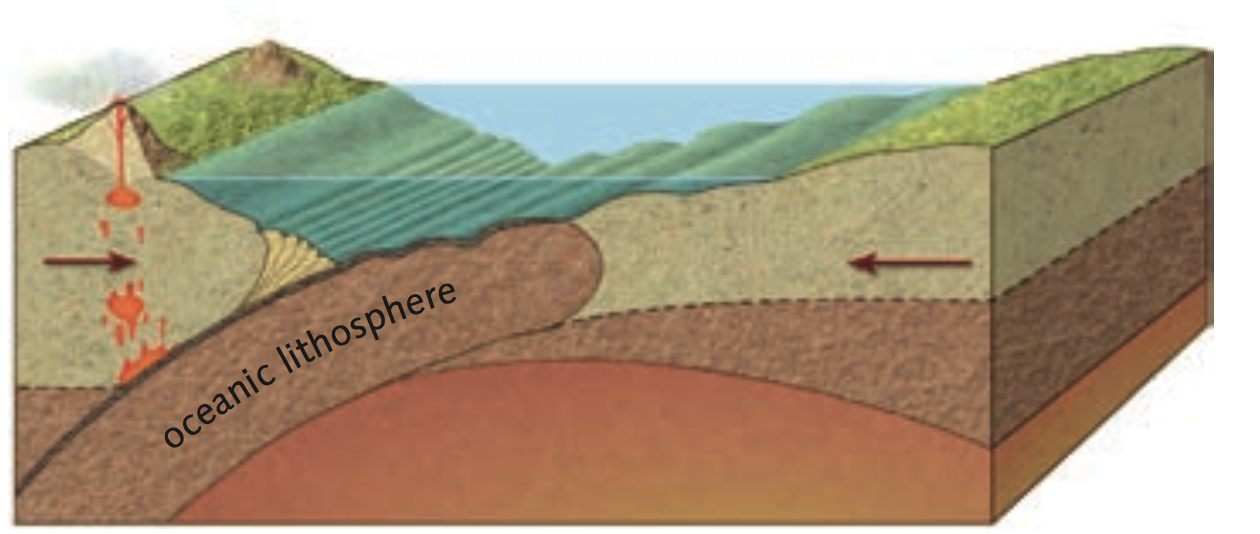
The Atlantic is an example of an expanding ocean. Its size is increasing steadily due to the production of new oceanic lithosphere (at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge) and the fact that it is no longer surrounded by subduction zones.
The oceanic lithosphere becomes progressively older the further it is from the ridge. It also becomes colder and denser. Eventually, this causes the lithosphere to sink down into the mantle, which results in the formation of trenches and subduction zones. From this stage onwards, the ocean, which until this point had been increasing in size, starts to shrink. This is the current situation in the Pacific Ocean, which has many trenches at its boundaries and is getting progressively smaller every year.
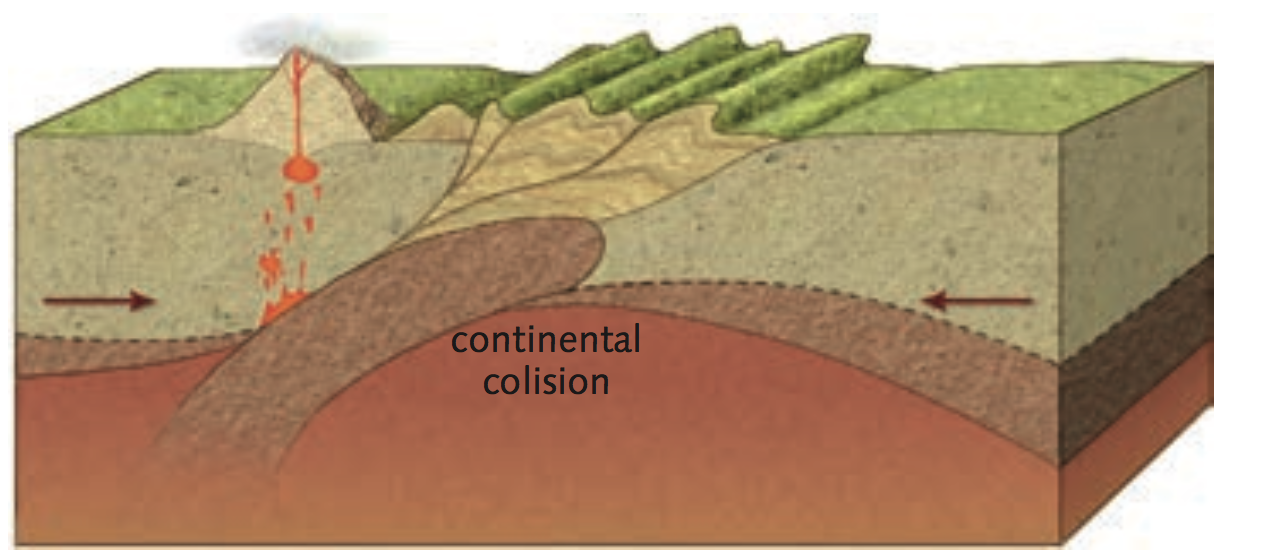
40 million years ago the Indian continent collided with the southern edge of Asia. Marine sediment had accumulated on the edge of both continents when there was an ocean between them. This sediment folded and deformed to create what is now the Himalayas. The marine fossil remains in these mountains are evidence that these rocks once formed part of an ancient ocean floor.

Activity 47
Understand
Activity 48
Analyse
Activity 49
Analyse
Activity 50
Analyse
Activity 51
Understand
Activity 52
Understand
Activity 53
Evaluate
Activity 54
Understand
Activity 55
Understand
Activity 56
Apply
Activity 57
Apply
Activity 58
Understand
Activity 59
Evaluate