We use cookies to improve and analyse your browsing experience on our web. You can accept these cookies, reject them or choose your settings by clicking on the corresponding buttons. Please note that rejecting cookies may affect your browsing experience. For more information you can consult our Cookies policy.
Cookies are an essential part of how our web works. The main goal of cookies is to make your browsing experience more comfortable and efficient and to improve our services and the web itself.
Here you can find all the information about the cookies we use and you can activate and/or deactivate them according to your preferences, except for those cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of the web. Blocking some cookies may affect your experience on the web and how the site works. For more information you can visit our Cookie Policy.
These Cookies are necessary for the web to function and cannot be disabled on our systems. They are generally only set up in response to actions you may take such as requesting services, setting your privacy preferences, logging in or completing forms. You can set your browser to block or warn you about these cookies, but some parts of the web will not work. Information about Cookies.
These Cookies allow us to count the number of visits and traffic sources so that we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to find out which pages are the most popular and least popular, and to see how visitors move around the web. All information collected by these Cookies is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these Cookies we will not know when you visited our web. Information about Cookies.
These cookies are used to analyse your activity in order to show you personalised advertisements.Information about Cookies.
Change theme

Revision mode

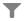
Inside the cell each organelle fulfills a function and they all work in a coordinated way. However, in the human body there are different types of cells that have a different morphology.
As cells multiply during their embryonic development, a process of cell differentiation occurs. Cell groups specialise so they can perform different tasks and different types of cells are created.
Cell differentiation involves changes at different levels:
Diversity of cellular forms

In order to increase their efficiency, cells of the same type group together. They collaborate in a common task and so they form a tissue. Tissues complete specific processes cells have specialised for.
Tissues are characterised by the type of cells that constitute them as well as the intercellular substance between them. A basic classification of tissues groups them according to the function they perform: epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous.
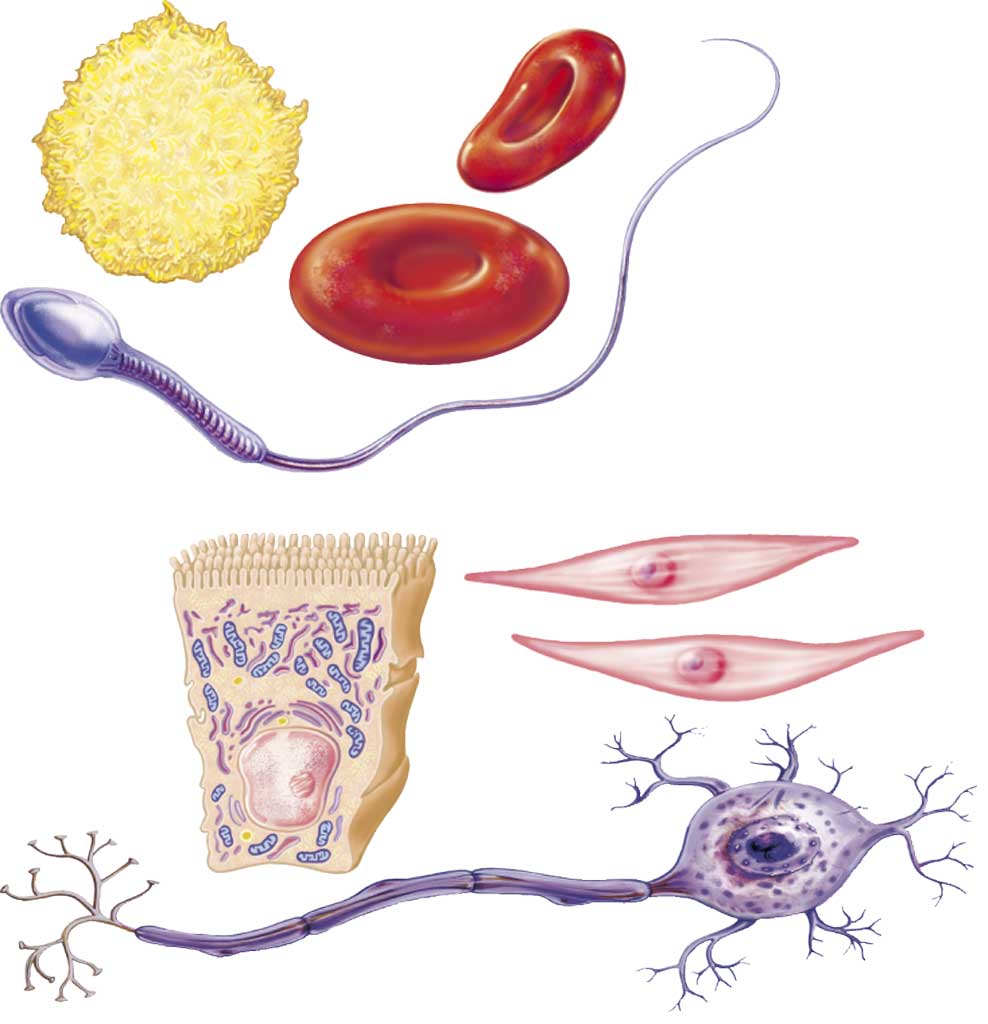
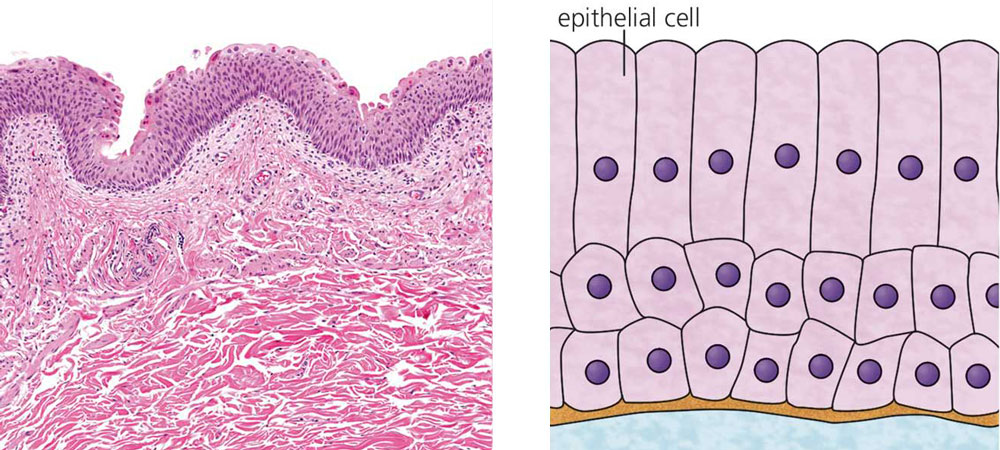
They cover the surface of the body, lining internal cavities and enveloping the different organs. Cells are arranged very closely together (there is almost no intercellular substance between them). According to their function, epithelial tissues are classified into various types: the epithelium tissue and the glandular epithelium.
The main function of connective tissues is to support, unify and connect systems in the organism.
Connective tissues have a large amount of extracellular matrix (set of substances found outside cells) in which they are embedded.
There are two types of connective tissues: non-specialised, which are connective, and specialised, including adipose, cartilage and bone tissue.
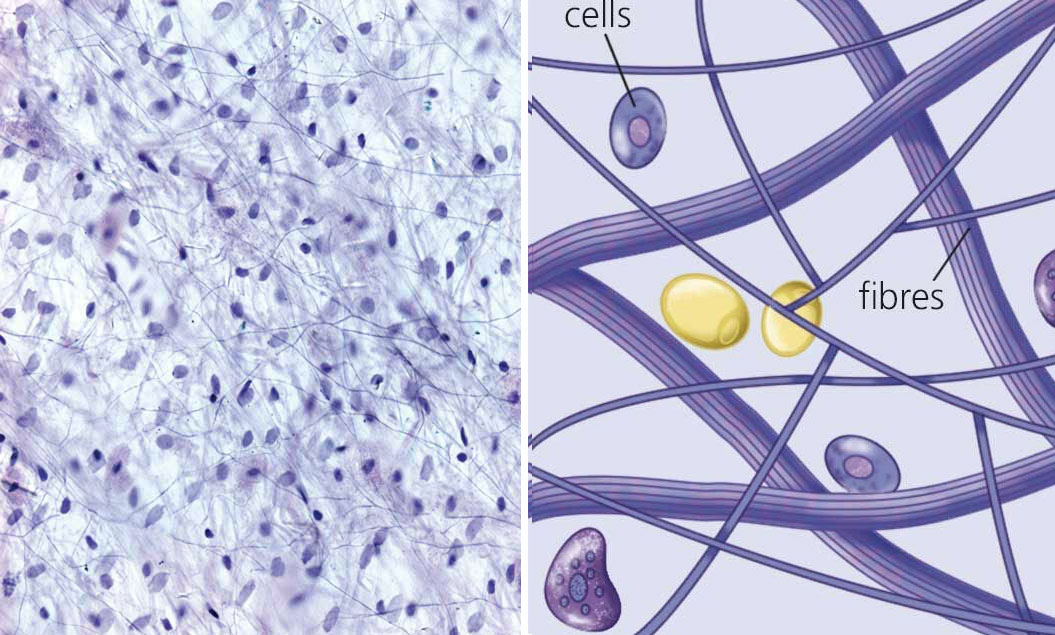
Connective tissue: located in the deepest layer of our skin, it constitutes the ‘stuffing’ between organs. The extracellular matrix contains many fibres, such as collagen.

Adipose tissue: composed of cells that accumulate fat. Their main function is to be an energy reserve, although it also has other functions.

Cartilaginous tissue: is a firm and elastic tissue, that protects joints from the bones, strengthens the larynx, trachea and forms structures such as the pinna or nose.
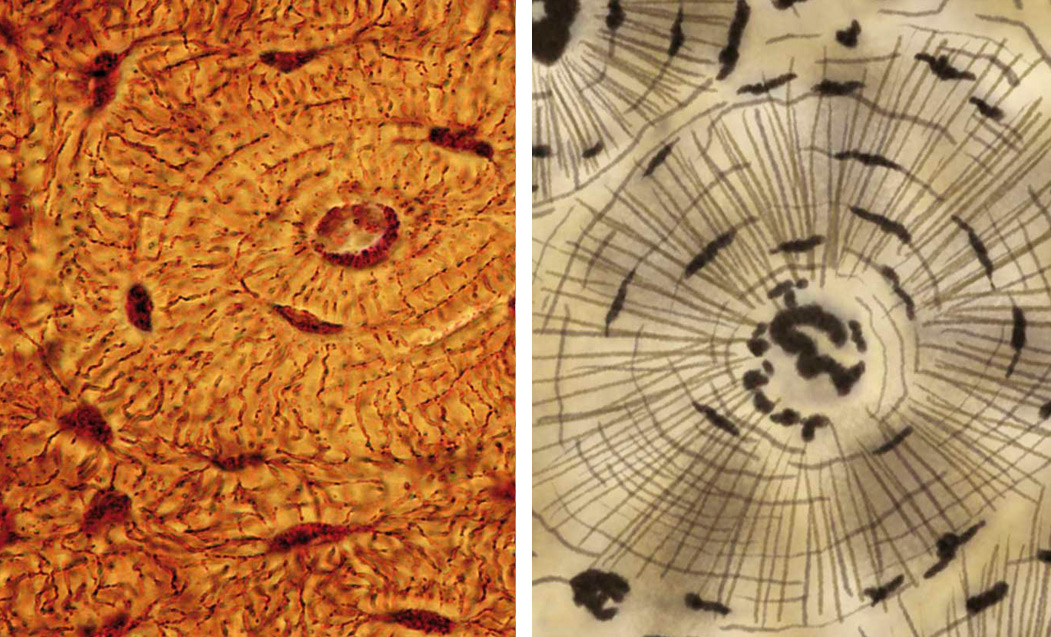
Bone tissue: is a rigid tissue, due to the great amount of minerals that are deposited in its matrix. It supports the organism.
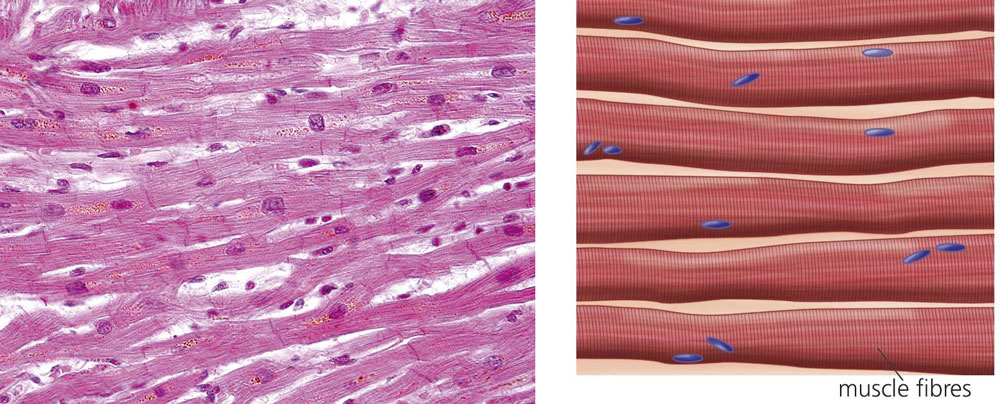
Muscle tissue is composed of special types of elongated cells called muscle fibres. Their most important characteristic is that they are able to contract and for this reason they are responsible for the organism's movement.
Muscle tissue that allows the skeleton to move is referred to as striated muscle tissue and they contract voluntarily. Smooth muscle tissue, which is responsible for the movements of organs such as the stomach or uterus, contracts involuntarily. Cardiac muscle tissue is a special type of tissue because it has striated fibres, but contracts involuntarily.
Nervous tissue is composed of very specialised cells called neurons, which transmit nerve impulses. The nervous system coordinates the functioning of the organism.

Tissues group together to form organs; as they do so, the functions each organ performs complement each other leading to even more complex functions. Displayed in the images below you can see some of the many organs humans have.

Key concepts
Activity 12
Which organelle would be more developed in a cell of the salivary glands?
Activity 13
Which cell has more mitochondria: a spermatozoid or an ovum?
Activity 14
Embryonic cells have the capacity to differentiate and reproduce indefinitely. In adult tissues certain cells keep these properties. They are mother cells. Investigate the importance of these particular cells for science and health and write a small report bellow.
Activity 15
Describe the shape of the cells represented in the image.
Activity 16
Apart from salivary glands, do you know any other glands?
Activty 17
Why do you think cells of epithelial tissues are close together, with almost no intercellular substance between them?
Activity 18
Mucus tends to be moist and thin. On the other hand, the epidermis is thicker and covered by a layer of dead cells. Explain why they are different.
Activity 19
Blood is a connective tissue.
Activity 20
What is the function of the cartilaginous tissue in the larynx and trachea?
Activity 21
Can you think of any other functions that adipose tissue performs, apart from being an energy reserve? Choose the correct answers.
Activity 22
Listen to the following statements and say true or false. Correct the false sentences.
Activity 23
Why do you think nerve cells have numerous branch-like extensions? Choose the correct answers.
Activity 24
Identify an organ that has: