We use cookies to improve and analyse your browsing experience on our web. You can accept these cookies, reject them or choose your settings by clicking on the corresponding buttons. Please note that rejecting cookies may affect your browsing experience. For more information you can consult our Cookies policy.
Cookies are an essential part of how our web works. The main goal of cookies is to make your browsing experience more comfortable and efficient and to improve our services and the web itself.
Here you can find all the information about the cookies we use and you can activate and/or deactivate them according to your preferences, except for those cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of the web. Blocking some cookies may affect your experience on the web and how the site works. For more information you can visit our Cookie Policy.
These Cookies are necessary for the web to function and cannot be disabled on our systems. They are generally only set up in response to actions you may take such as requesting services, setting your privacy preferences, logging in or completing forms. You can set your browser to block or warn you about these cookies, but some parts of the web will not work. Information about Cookies.
These Cookies allow us to count the number of visits and traffic sources so that we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to find out which pages are the most popular and least popular, and to see how visitors move around the web. All information collected by these Cookies is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these Cookies we will not know when you visited our web. Information about Cookies.
These cookies are used to analyse your activity in order to show you personalised advertisements. Information about Cookies.
Change theme

Revision mode

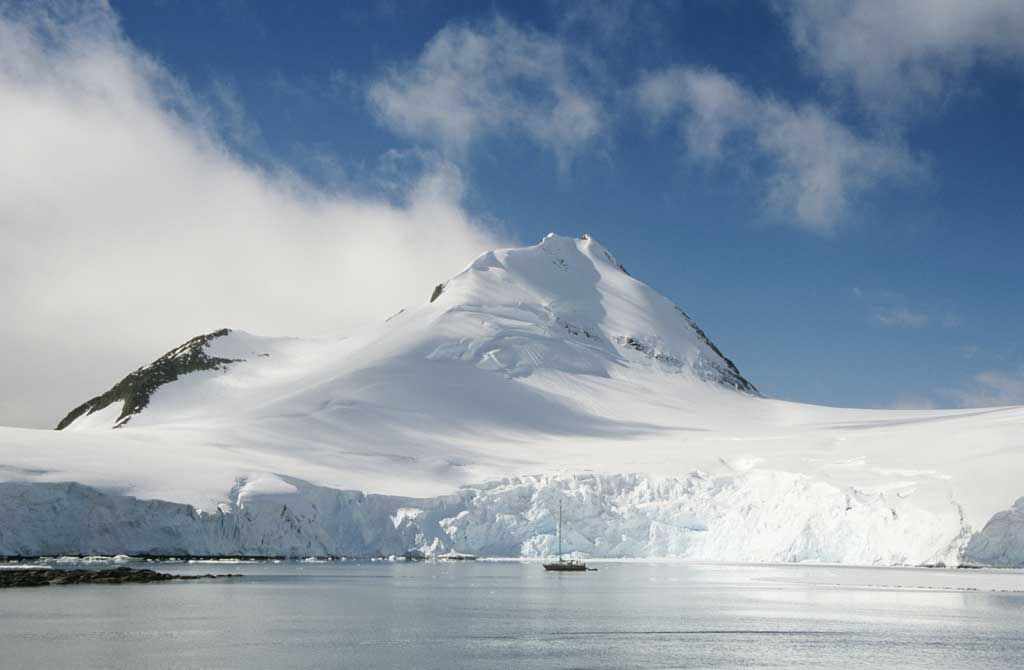
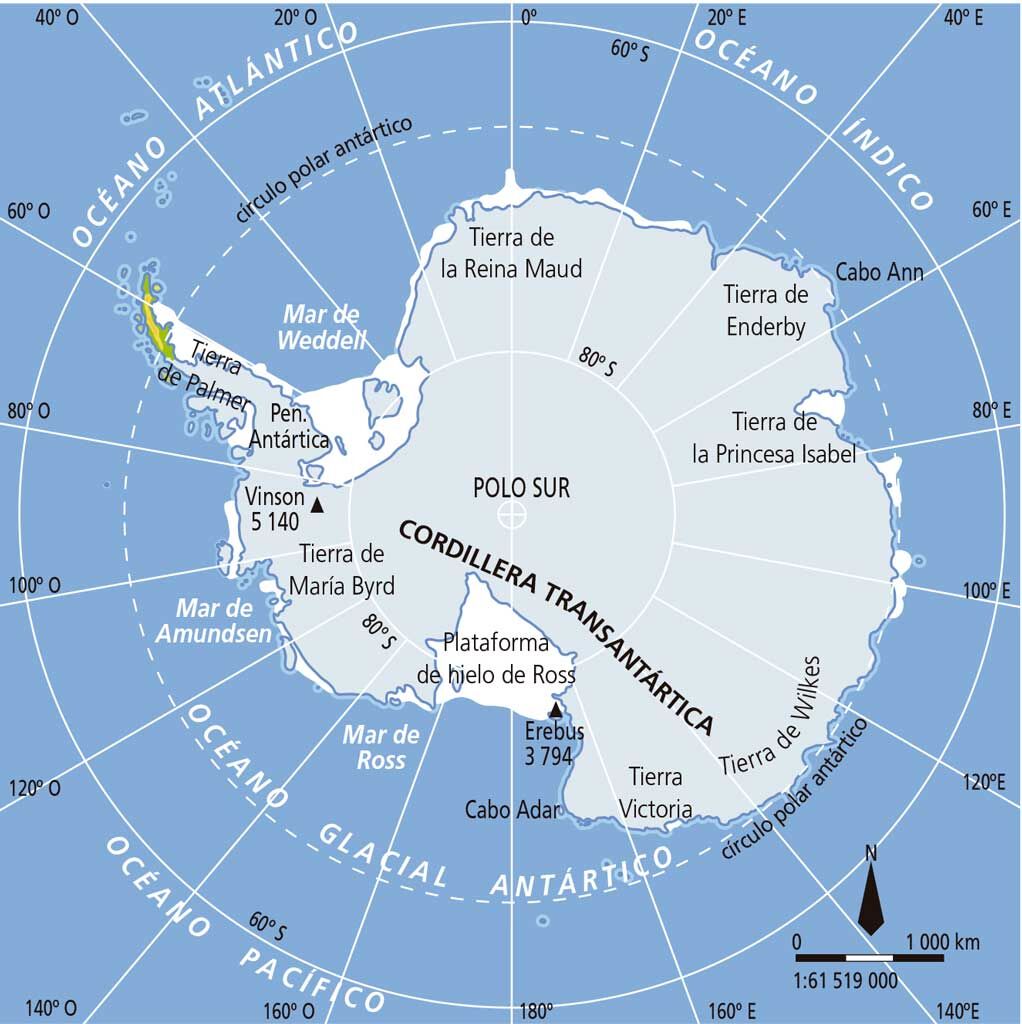
El continente de la Antártida tiene una extensión de unos 14 millones de km2 y está recubierto por una gran masa de hielo, cuyo espesor llega a más de 4 000 m en algunos puntos y supone el 80 % del agua dulce del planeta. Sobre la masa de hielo destaca la cordillera Transantártica y montes, como el Vinson (4 897 m).
La Antártida fue el último continente en ser explorado. Su descubridor fue probablemente el español Gabriel de Castilla (1603) y el primero que la circunnavegó fue el británico James Cook (1772). En 1911 el noruego Roald Amundsen fue el primero en llegar al polo sur. El Tratado Antártico, firmado en Washington (1959) controla la explotación de los recursos de este continente.
El clima de la Antártida es polar extremo, con escasas precipitaciones, por la ausencia de evaporación, y temperaturas bajísimas (en el monte Argus se ha registrado -93,2 ºC, la temperatura más baja del planeta). Además, es el continente de mayor altitud media: 2 030 m. En cuanto a su fauna es casi exclusivamente marina o bien se alimenta en el mar: focas, pingüinos, lobos marinos, ballenas y orcas.

Orcas.

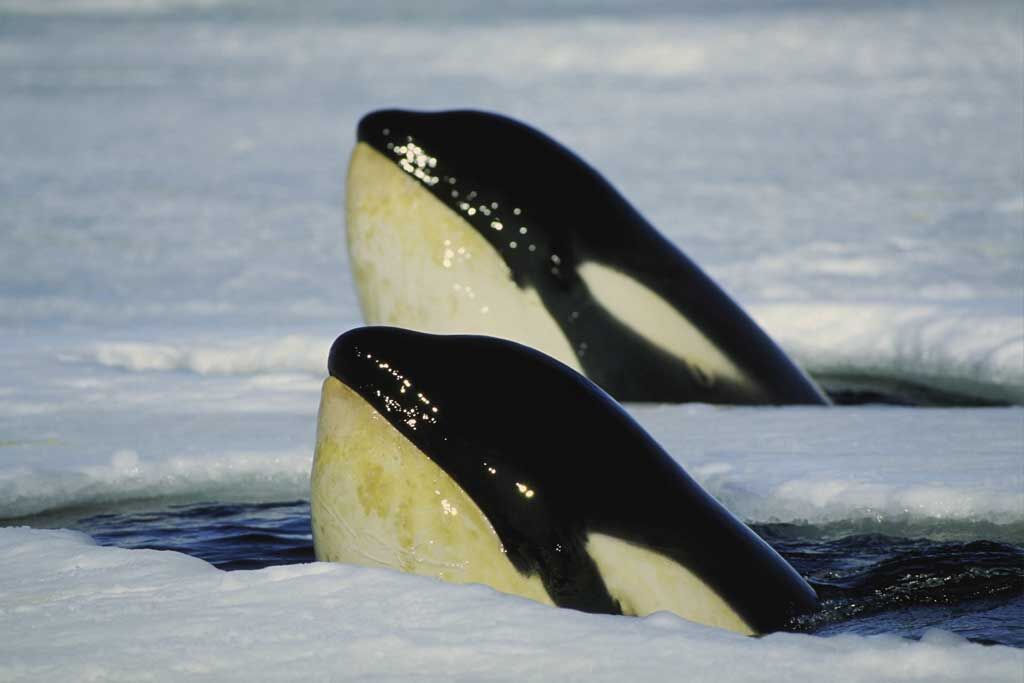
Paisaje antártico.
Actividad 22
Observa el mapa físico de Australia. ¿Qué características tiene su relieve? ¿Qué mar la separa de Nueva Zelanda?
Actividad 23
Explica qué climas se dan en la costa oriental australiana y pon algunos ejemplos de la vegetación y fauna características de cada uno de ellos.
Actividad 24
Lee en la página web Infraestructuras para la investigación polar sobre las bases científicas españolas que hay en la Antártida. ¿Dónde se localizan? ¿A qué se dedican? ¿Cuándo comenzaron a funcionar?